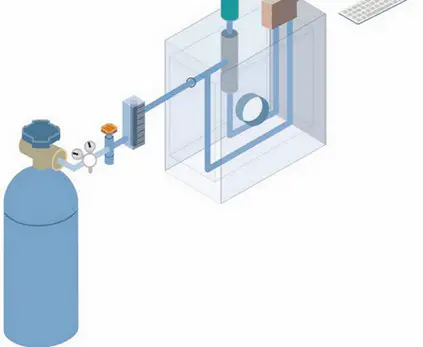

It is a term used to describe analytical separation methods used to check volatile substances in their gas phase. What happens during gas chromatography is that the components of a sample are dissolved in a solvent and vaporized to separate the analytes. It is made possible by distributing the sample into two phases:
The gas chromatography is the only form of chromatography that does not use the mobile phase when interacting with the analyte. For gas chromatography to take place a gas chromatograph has to be used. (1, 2, and 3)
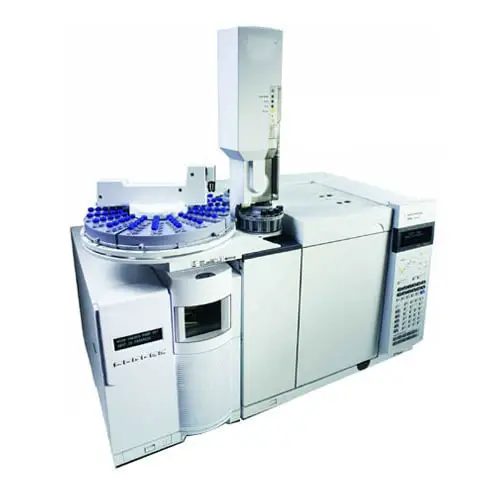

Image 2: An actual gas chromatograph device.
Picture Source: imimg.com
It is an analytical instrument used to measure the content of different components in a given sample.
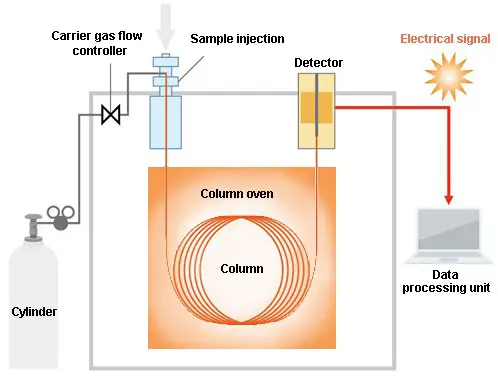
Image 3: The image above shows how gas chromatography works (diagram).
Picture Source: shimadzu.com
The sample solution is placed into the gas chromatograph and enters the gas stream which transports the sample into the column (separation tube). A carrier gas is used in the form of helium or nitrogen. The components of the sample are separated inside the column.
The number of components that exit the column is measured by the detector. If a sample with an unknown concentration is measured, a standard sample with known concentration is being injected into the gas chromatograph. (2, 3, 4, and 5)
Gas chromatography was discovered in the early 1900s by Mikhail Semenovich Tsvett. He used it as a separation method of separating compounds. Liquid-solid column chromatography is used to separate the organic compounds in a given solution.
There are different types of gas chromatography, but the most commonly used method in separating organic compounds in gas-liquid chromatography.
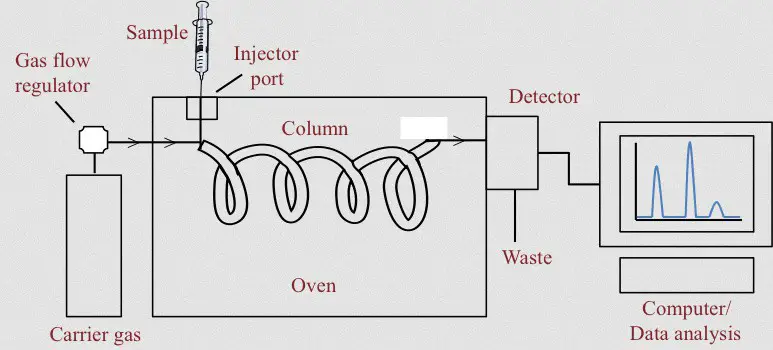
Image 4: The image above outlines the different components of gas chromatography (diagram).
Picture Source: bitesizebio.com
Which carrier gas to choose? It depends on the type of detector.
a. Packed columns – It has a divided, inert, and solid support material coated with the liquid stationary phase.
b. Capillary columns – It has an internal diameter that is about a few tenths of a millimeter. It could be a wall-coated (has a papillary tube with walls coated with liquid stationary phase) or open tubular or support-coated open tubular (the capillary’s inner wall has a thin layer of support material like diatomaceous earth wherein the stationary phase is absorbed). (2, 5, 7, and 8)
The two types of capillary columns are more efficient than the packed columns, but the support-coated open tubular is less efficient than the wall-coated open tubular.
 gas chromatograph with a mass spectrometer" width="400" height="230" />
gas chromatograph with a mass spectrometer" width="400" height="230" />
Image 5:A gas chromatograph with a mass spectrometer.
Picture Source: utm.my
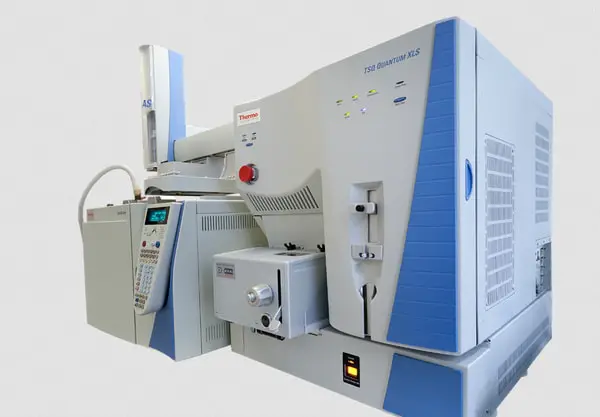 gas chromatograph with a flame ionization detector" width="400" height="278" />
gas chromatograph with a flame ionization detector" width="400" height="278" />
Image 6: A gas chromatograph with a flame ionization detector.
Picture Source: forschungsinfrastruktur.bmbwf.gv.at

Image 7: A gas chromatography with a thermal conductivity detector.
Picture Source: directindustry.com
 gas chromatograph with electron capture detector" width="500" height="289" />
gas chromatograph with electron capture detector" width="500" height="289" />
Image 8: A gas chromatograph with electron capture detector.
Picture Source: made-in-china.com
What detectors are used in a gas chromatograph?
Factors that could affect the separation of components
There are different factors that could significantly influence the separation of components. They are the following:
∙ Vapor pressure – The polarity of a particular compound can greatly affect its boiling point. The vapor pressure is high is the boiling point is low. The retention time is shorter because the compound being examined spends more time in the gas state. Hence, a low boiling solvent is typically used to dissolve a given sample.
∙ Polarity of components vs polarity of the stationary phase on the column – the retention time increases if the compound and stationary phase’s polarity is the same. A polar compound has a long retention time on its polar stationary phase. However, the retention time is shorter on the non-polar columns of the same temperature.
∙ Column temperature – A too high column temperature could lead to an extremely short retention time but yields in a poor separation because the majority of the components stay in the gas phase. For the components to be separated, it needs to interact with the stationary phase. If it won’t, then it could lead to a decrease in retention time. On top of it, the quality of separation deteriorates.
∙ Rate of carrier gas flow – The retention time is reduced significantly at a high flow rate. However, it would yield a poor separation as the component takes little time to interact with the stationary phase. The components are just pushed through the column.
∙ Length of the column – the separation is better in the longer column than the shorter column. With a lengthy column, the retention times increases and a peak broadening is observed secondary to increased longitudinal diffusion inside the column. It is because of the principle that the molecules of gasses do not only travel in one direction. They also travel backward and sideways.
∙ Amount of material injected – A poor separation is observed if you inject too much sample in the gas chromatograph. There is no need to inject too many samples as the detectors are highly sensitive. They can detect even just a small sample. (2, 4, 6, 9, and 10)
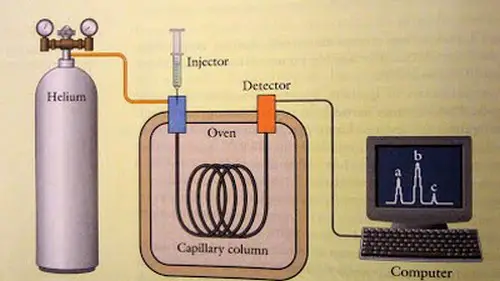
Image 9:A gas chromatography is essential in forensic science.
Picture Source: sites.google.com
Gas chromatography is useful in forensic science. it is used through the following ways:
Forensic pathology – The ability of gas chromatography to identify individual elements and molecules in a given compound can be extremely useful in forensic pathology. It helps in determining the fluids and compounds present in the human body after death.
It is essential in finding out whether the person was intoxicated from alcohol or drug at the time of death. It also helps detect if there is a poison or other harmful substances in the human body. It helps in finding out the possible cause of death and the motive and culprit, especially if foul play is suspected.
Crime scene testing – A gas chromatography is integral in checking the sample in a crime scene. It tests all possible samples such as blood, fiber from clothing, and other materials. It will enable the scientist to determine what and who were present in the crime scene.
It will help the authority to come up with theories about the suspect and what transpires before the crime. With gas chromatography, the error of margin is close to none making it a substantial evidence in court.
Arson investigation – A gas chromatography is helpful when investigating for arson. In the United States, arson is one of the leading causes of fires and the second cause of injuries and death. To start a fire, you would need different compounds and components.
The number of compounds and components depends on the strength and concentration. It is important to note that many compounds are dissolved during the fire. A gas chromatography is a low-cost alternative to identifying flammable liquids on-site. (1, 4, 6, 9, and 10)
References